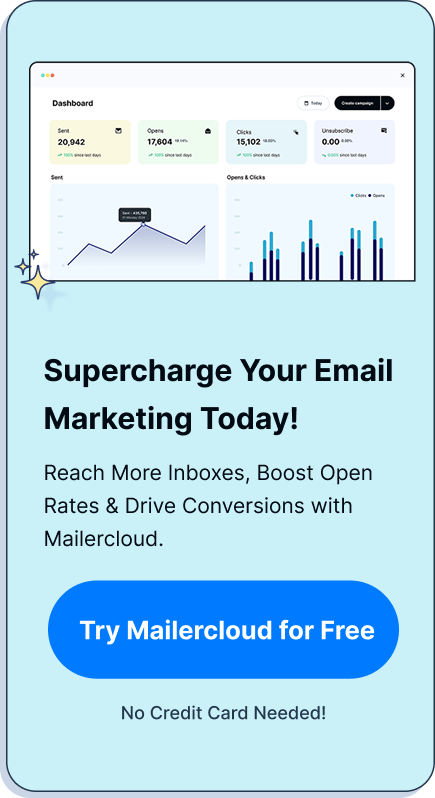
Unleash the power of email communication with this comprehensive guide to email formatting. Whether you’re crafting a formal business email or a more informal message, understanding the right format can make your emails more impactful and easier to read. Stick around to discover email format examples, best practices, and templates that will elevate your email game.
Table of Contents
Understanding Email Formats
There is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to email formats. Different situations call for different email styles. Whether it’s a quick update to a colleague, a formal proposal to a client, or an email marketing campaign, each requires a distinct format. Understanding these differences and knowing how to use them effectively is essential for successful communication.
What Defines a Formal Email?
A formal email typically follows a certain format, including elements like a professional greeting, clear and concise body text, and an official sign-off. The tone and language used in a formal email should be polite and professional. This type of email message is often used in business communication, when applying for a job, or when writing to someone you don’t know well.
What Makes Up the Subject Line?
The subject line of an email sets the tone for the reader and provides them with an idea of what to expect in the body of the email. A well-crafted subject line can increase open rates and ensure your message gets through the cluttered inbox.
Salutation: Setting the Tone for Your Email
The salutation in an email is the greeting that sets the tone for the rest of your correspondence. In formal emails, it’s important to use a professional salutation like “Dear [Recipient Name].” Using the recipient’s name makes your email more personal and shows respect.
Crafting a Professional Email: What’s the Format?
A professional email format typically includes a subject line, salutation, body text, and sign-off. The body of your email should clearly convey your message in a concise manner. Always proofread your email and ensure that you are following email etiquette before sending it to ensure it is free from errors and clearly communicates your message.
Here are some best practices for email formatting:
- Subject Line: Keep it clear, concise, and relevant to the content of the email.
- Salutation: Start with a proper greeting.
- Body: Keep paragraphs short and use bullet points or numbered lists for clarity. Each paragraph should cover one idea or topic.
- Use of Bold & Italics: Use them sparingly to emphasize important points.
- Attachments: Make sure to mention any attachments in the body of the email.
- Closing: Close with a professional sign-off like “Best regards” or “Sincerely”, followed by your name.
- Signature: Include a professional signature with your contact information.
- Review: Always proofread your email for grammar, spelling, and clarity before hitting send.
Remember, tone can be easily misunderstood in emails. Be polite and professional, avoid using all caps (it can come across as shouting), and be careful with humor and sarcasm as it may not translate well.
Effective Email Writing: Tips and Examples
Writing powerful emails is a skill anyone can learn with practice. Techniques like breaking up text with bullet points or subheadings can make your emails more readable. It’s also important to keep your emails concise, focusing on the purpose of your message.
Effective email writing requires clarity, precision, and a keen understanding of your audience. Here are some useful tips and examples to guide you in crafting emails:
- Your subject line should be a concise summary of the email’s content. Example: Instead of “Meeting”, use “Marketing Team Meeting: Friday, Oct 20, 10 AM”
- Start with a professional salutation that fits your relationship with the recipient. Example: “Dear Mr. Smith,” or “Hello Jane,”
- Clearly state the purpose of the email in the first few lines. Example: “I am writing to discuss our upcoming marketing campaign.”
- Avoid jargon and complex sentences. Keep your language simple and direct. Example: Instead of “The utilization of our resources has been suboptimal lately”, use “We’re not using our resources effectively.”
- If you have multiple points to address, bullet points or numbered lists can make your email easier to read. Example:
- Point 1: Discuss marketing campaign.
- Point 2: Review budget report.
- Point 3: Finalize team assignments.
- If you require a response or action from the recipient, make it clear. Example: “Please review the attached report and provide your feedback by Wednesday.”
- End your email with a polite closing and your name. Example: “Best regards, [Your Name]”
- Always proofread your email for grammar, spelling mistakes, and clarity before pressing send.
Remember that practice makes perfect. The more you apply these tips, the better your email communication skills will become.
Creating a Template: The Power of Standardization
Having standardized email templates can save you time and ensure consistency in your email communications. A good template includes all the essential elements of an email — subject line, salutation, body text, sign-off and an email signature if necessary— and offers a solid structure that you can adapt for different purposes.
Conciseness: The Key to Effective Emails
Concise writing is key to email communication. Your recipient should be able to quickly read and understand the purpose of your email. Conciseness also shows respect for your recipient’s time, as it allows them to grasp your message in a shorter time frame.
Make sure your subject line accurately represents the content of the email. Each email should cover only one topic or purpose. This prevents confusion and makes it easier for the recipient to respond effectively. If you need a response or action from the recipient, state this clearly and concisely. Ensure there are no unnecessary words or sentences. Every word should serve a purpose. However, if you have ended up writing an email that you think is still long enough for the readers. Then you can quickly condense it with the help of an AI summarizer. It will remove all the unnecessary words and provide you with a concise version.
Best Practices for Your Call to Action
A call to action (CTA) prompts your recipient to take a specific action. It’s an essential element of business emails, marketing campaigns, and any email where you need the recipient to do something. A clear, concise CTA can greatly increase the chances of your email achieving its goal.
- Be Specific: Your CTA should be clear and specific. Tell your audience exactly what you want them to do.
- Use Actionable Language: Use strong, compelling verbs that encourage action. For example, “Buy Now”, “Sign Up”, or “Download Here”.
- Make it Stand Out: Your CTA should be visually striking with font, color, and size that makes it stand out from the rest of your content.
- Create Urgency: Creating a sense of urgency can encourage users to act immediately rather than delaying action. Use phrases like “Limited Time Offer” or “Don’t Miss Out”.
- Keep it Simple: A complicated CTA can confuse your audience and reduce the chances of conversion. Keep your language simple and straightforward.
- Placement Matters: Position your CTA where it’s easy to find and click. High visibility leads to higher conversion rates.
- Test and Tweak: Test different CTAs to see what works best with your audience. Experiment with different colors, texts, and placements, then stick with what gets the most engagement.

Remember, an effective CTA is crucial for achieving your marketing goals, whether it’s increasing subscriptions, sales, or other types of engagement.
Informal Emails: When and How to Use Them
Informal emails follow less strict rules than their formal counterparts. They are usually sent to people you know well — friends, family, or close coworkers. An informal email might use colloquial language, emoticons, and less formal salutations.
The language used in an informal email can be relaxed and conversational, often reflecting the writer’s personality. Emoticons, abbreviations, and slangs are commonly accepted. However, even though the email is informal, good grammar and correct spelling should still be maintained to ensure clarity and prevent misunderstandings.
Key Takeaways
- Different situations call for different email formats.
- Formal emails require professional language and a specific structure.
- The subject line and salutation set the tone for your email.
- Informal emails can use more casual language and formatting.
- Effective emails are concise and clear.
- Templates can streamline your email writing process.
- Every email with a purpose should end with a clear call to action.
Lina is a content writer with a passion for reading, writing, and cooking. She aims to explore the world of words and flavors. With a deep love for literature and a knack for creating mouthwatering recipes, she strive to engage and inspire others through her work.